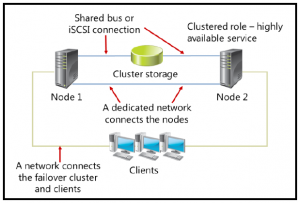
A failover cluster is a pair or group of Windows servers that work together to make applications and services highly available. The servers in a failover cluster are called nodes. If a node in a cluster fails or becomesunavailable, another node in the same failover cluster starts providing the services that the failed node was offering. This process is called failover and it results in minimal (or in certain cases, no) service disruptions forclients that are accessing the service. Failover clusters also provide CSV functionality, which provides a common namespace that you can use to access shared storage from all nodes.
Failover clustering has several components, including the following:
|
• |
Nodes. Nodes are Windows Server computers that are members of a failover cluster. These computers have the failover clustering feature installed, and they run highly available services, applications, and otherresources that are associated with a cluster. A failover cluster in Windows Server 2012 R2 can have up to 64 nodes, which can run up to 8,000 virtual machines. A single node can run up to 1,024 virtual machines. |
|
• |
Networks. Networks enable communication between nodes that are still available and responsive, and also between nodes and client computers. Because clusters use external storage such as iSCSI or Fibre ChannelStorage Area Network (SAN), nodes also use networks for accessing the shared storage. |
|
• |
Clustered role. A clustered role is a highly available role or service that is running on the cluster node and to which clients connect. If such a service becomes unavailable on one node, the failover cluster fails it overautomatically to another node and redirects client requests for the service to the new node. |
|
• |
Resources. Resources are physical or logical elements such as a shared folder, disk, or IP address, which the failover cluster manages. Resources may provide service to clients or may be integral parts of highlyavailable applications. Resources are the most basic and smallest configurable units. A resource can run only on a single node at any given time. |
|
• |
Cluster Storage. Each node has local storage (where the Windows operating system is installed), in addition to server roles and highly available applications. Cluster storage is a shared storage, where applicationconfiguration and data is stored. When a node fails, other nodes can access data on the cluster storage, and can start applications from that point. For example, the highly available virtual machine storesconfiguration data and virtual hard disks of the highly available virtual machine are stored on the cluster storage. |
|
• |
Clients. These are computers that access highly available services and applications that are running in the failover cluster. There should be multiple network paths between clients and the cluster. Clients should alsotry to reconnect to the service automatically if a cluster node fails. |
In a failover cluster, each node in the cluster:
|
• |
Has full connectivity and communication with other failover cluster nodes. |
|
• |
Is aware of configuration changes to the failover cluster, such as when an additional node joins or leaves the cluster. Each node is also aware of other node failures, and has the ability to run services that the failednode hosted. You can configure which services to run on which nodes. |
|
• |
Connects to a network through which client computers can access the node. |
|
• |
Connects to other nodes, and regularly checks their availability and responsiveness. |
|
• |
Connects to shared storage, where configuration and data of highly available applications is stored. |
|
• |
Has awareness of the services and applications that are running locally, and resources that are running on other failover cluster nodes. |